JavaNIO寫大文件對比(win7和mac)
測試說明
創新互聯建站服務項目包括寧蒗網站建設、寧蒗網站制作、寧蒗網頁制作以及寧蒗網絡營銷策劃等。多年來,我們專注于互聯網行業,利用自身積累的技術優勢、行業經驗、深度合作伙伴關系等,向廣大中小型企業、政府機構等提供互聯網行業的解決方案,寧蒗網站推廣取得了明顯的社會效益與經濟效益。目前,我們服務的客戶以成都為中心已經輻射到寧蒗省份的部分城市,未來相信會繼續擴大服務區域并繼續獲得客戶的支持與信任!
寫2G文件,分批次寫入,每批次寫入128MB;
分別在Win7系統(3G內存,雙核,32位,T系列處理器)和MacOS系統(8G內存,四核,64位,i7系列處理器)下運行測試。理論上跟硬盤類型和配置也有關系,這里不再貼出了。
測試代碼
package rwbigfile;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Channels;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode;
import java.nio.channels.ReadableByteChannel;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedAction;
import util.StopWatch;
/**
* NIO寫大文件比較
* @author Will
*
*/
public class WriteBigFileComparison {
// data chunk be written per time
private static final int DATA_CHUNK = 128 * 1024 * 1024;
// total data size is 2G
private static final long LEN = 2L * 1024 * 1024 * 1024L;
public static void writeWithFileChannel() throws IOException {
File file = new File("e:/test/fc.dat");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = raf.getChannel();
byte[] data = null;
long len = LEN;
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(DATA_CHUNK);
int dataChunk = DATA_CHUNK / (1024 * 1024);
while (len >= DATA_CHUNK) {
System.out.println("write a data chunk: " + dataChunk + "MB");
buf.clear(); // clear for re-write
data = new byte[DATA_CHUNK];
for (int i = 0; i < DATA_CHUNK; i++) {
buf.put(data[i]);
}
data = null;
buf.flip(); // switches a Buffer from writing mode to reading mode
fileChannel.write(buf);
fileChannel.force(true);
len -= DATA_CHUNK;
}
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println("write rest data chunk: " + len + "B");
buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect((int) len);
data = new byte[(int) len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
buf.put(data[i]);
}
buf.flip(); // switches a Buffer from writing mode to reading mode, position to 0, limit not changed
fileChannel.write(buf);
fileChannel.force(true);
data = null;
}
fileChannel.close();
raf.close();
}
/**
* write big file with MappedByteBuffer
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void writeWithMappedByteBuffer() throws IOException {
File file = new File("e:/test/mb.dat");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = raf.getChannel();
int pos = 0;
MappedByteBuffer mbb = null;
byte[] data = null;
long len = LEN;
int dataChunk = DATA_CHUNK / (1024 * 1024);
while (len >= DATA_CHUNK) {
System.out.println("write a data chunk: " + dataChunk + "MB");
mbb = fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, pos, DATA_CHUNK);
data = new byte[DATA_CHUNK];
mbb.put(data);
data = null;
len -= DATA_CHUNK;
pos += DATA_CHUNK;
}
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println("write rest data chunk: " + len + "B");
mbb = fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, pos, len);
data = new byte[(int) len];
mbb.put(data);
}
data = null;
unmap(mbb); // release MappedByteBuffer
fileChannel.close();
}
public static void writeWithTransferTo() throws IOException {
File file = new File("e:/test/transfer.dat");
if (file.exists()) {
file.delete();
}
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
FileChannel toFileChannel = raf.getChannel();
long len = LEN;
byte[] data = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bais = null;
ReadableByteChannel fromByteChannel = null;
long position = 0;
int dataChunk = DATA_CHUNK / (1024 * 1024);
while (len >= DATA_CHUNK) {
System.out.println("write a data chunk: " + dataChunk + "MB");
data = new byte[DATA_CHUNK];
bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(data);
fromByteChannel = Channels.newChannel(bais);
long count = DATA_CHUNK;
toFileChannel.transferFrom(fromByteChannel, position, count);
data = null;
position += DATA_CHUNK;
len -= DATA_CHUNK;
}
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println("write rest data chunk: " + len + "B");
data = new byte[(int) len];
bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(data);
fromByteChannel = Channels.newChannel(bais);
long count = len;
toFileChannel.transferFrom(fromByteChannel, position, count);
}
data = null;
toFileChannel.close();
fromByteChannel.close();
}
/**
* 在MappedByteBuffer釋放后再對它進行讀操作的話就會引發jvm crash,在并發情況下很容易發生
* 正在釋放時另一個線程正開始讀取,于是crash就發生了。所以為了系統穩定性釋放前一般需要檢
* 查是否還有線程在讀或寫
* @param mappedByteBuffer
*/
public static void unmap(final MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer) {
try {
if (mappedByteBuffer == null) {
return;
}
mappedByteBuffer.force();
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("restriction")
public Object run() {
try {
Method getCleanerMethod = mappedByteBuffer.getClass()
.getMethod("cleaner", new Class[0]);
getCleanerMethod.setAccessible(true);
sun.misc.Cleaner cleaner =
(sun.misc.Cleaner) getCleanerMethod
.invoke(mappedByteBuffer, new Object[0]);
cleaner.clean();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("clean MappedByteBuffer completed");
return null;
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch();
sw.startWithTaskName("write with file channel's write(ByteBuffer)");
writeWithFileChannel();
sw.stopAndPrint();
sw.startWithTaskName("write with file channel's transferTo");
writeWithTransferTo();
sw.stopAndPrint();
sw.startWithTaskName("write with MappedByteBuffer");
writeWithMappedByteBuffer();
sw.stopAndPrint();
}
}測試結果(Y軸是耗時秒數)
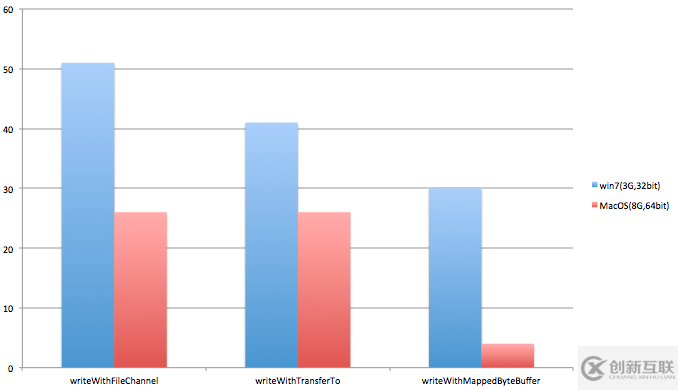
- 顯然writeWithMappedByteBuffer方式性能最好,且在硬件配置較高情況下優勢越加明顯
- 在硬件配置較低情況下,writeWithTransferTo比writeWithFileChannel性能稍好
- 在硬件配置較高情況下,writeWithTransferTo和writeWithFileChannel的性能基本持平
- 此外,注意writeWithMappedByteBuffer方式除了占用JVM堆內存外,還要占用額外的native內存(Direct Byte Buffer內存)
內存映射文件使用經驗
MappedByteBuffer需要占用“雙倍”的內存(對象JVM堆內存和Direct Byte Buffer內存),可以通過-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize參數設置后者最大大小
不要頻繁調用MappedByteBuffer的force()方法,因為這個方法會強制OS刷新內存中的數據到磁盤,從而只能獲得些微的性能提升(相比IO方式),可以用后面的代碼實例進行定時、定量刷新
如果突然斷電或者服務器突然Down,內存映射文件數據可能還沒有寫入磁盤,這時就會丟失一些數據。為了降低這種風險,避免用MappedByteBuffer寫超大文件,可以把大文件分割成幾個小文件,但不能太小(否則將失去性能優勢)
ByteBuffer的rewind()方法將position屬性設回為0,因此可以重新讀取buffer中的數據;limit屬性保持不變,因此可讀取的字節數不變
ByteBuffer的flip()方法將一個Buffer由寫模式切換到讀模式
ByteBuffer的clear()和compact()可以在我們讀完ByteBuffer中的數據后重新切回寫模式。不同的是clear()會將position設置為0,limit設為capacity,換句話說Buffer被清空了,但Buffer內的數據并沒有被清空。如果Buffer中還有未被讀取的數據,那調用clear()之后,這些數據會被“遺忘”,再寫入就會覆蓋這些未讀數據。而調用compcat()之后,這些未被讀取的數據仍然可以保留,因為它將所有還未被讀取的數據拷貝到Buffer的左端,然后設置position為緊隨未讀數據之后,limit被設置為capacity,未讀數據不會被覆蓋
定時、定量刷新內存映射文件到磁盤
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class MappedFile {
// 文件名
private String fileName;
// 文件所在目錄路徑
private String fileDirPath;
// 文件對象
private File file;
private MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer;
private FileChannel fileChannel;
private boolean boundSuccess = false;
// 文件最大只能為50MB
private final static long MAX_FILE_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 50;
// 最大的臟數據量512KB,系統必須觸發一次強制刷
private long MAX_FLUSH_DATA_SIZE = 1024 * 512;
// 最大的刷間隔,系統必須觸發一次強制刷
private long MAX_FLUSH_TIME_GAP = 1000;
// 文件寫入位置
private long writePosition = 0;
// 最后一次刷數據的時候
private long lastFlushTime;
// 上一次刷的文件位置
private long lastFlushFilePosition = 0;
public MappedFile(String fileName, String fileDirPath) {
super();
this.fileName = fileName;
this.fileDirPath = fileDirPath;
this.file = new File(fileDirPath + "/" + fileName);
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
*
* 內存映照文件綁定
* @return
*/
public synchronized boolean boundChannelToByteBuffer() {
try {
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
this.fileChannel = raf.getChannel();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
this.boundSuccess = false;
return false;
}
try {
this.mappedByteBuffer = this.fileChannel
.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, MAX_FILE_SIZE);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
this.boundSuccess = false;
return false;
}
this.boundSuccess = true;
return true;
}
/**
* 寫數據:先將之前的文件刪除然后重新
* @param data
* @return
*/
public synchronized boolean writeData(byte[] data) {
return false;
}
/**
* 在文件末尾追加數據
* @param data
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public synchronized boolean appendData(byte[] data) throws Exception {
if (!boundSuccess) {
boundChannelToByteBuffer();
}
writePosition = writePosition + data.length;
if (writePosition >= MAX_FILE_SIZE) { // 如果寫入data會超出文件大小限制,不寫入
flush();
writePosition = writePosition - data.length;
System.out.println("File="
+ file.toURI().toString()
+ " is written full.");
System.out.println("already write data length:"
+ writePosition
+ ", max file size=" + MAX_FILE_SIZE);
return false;
}
this.mappedByteBuffer.put(data);
// 檢查是否需要把內存緩沖刷到磁盤
if ( (writePosition - lastFlushFilePosition > this.MAX_FLUSH_DATA_SIZE)
||
(System.currentTimeMillis() - lastFlushTime > this.MAX_FLUSH_TIME_GAP
&& writePosition > lastFlushFilePosition) ) {
flush(); // 刷到磁盤
}
return true;
}
public synchronized void flush() {
this.mappedByteBuffer.force();
this.lastFlushTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastFlushFilePosition = writePosition;
}
public long getLastFlushTime() {
return lastFlushTime;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
public String getFileDirPath() {
return fileDirPath;
}
public boolean isBundSuccess() {
return boundSuccess;
}
public File getFile() {
return file;
}
public static long getMaxFileSize() {
return MAX_FILE_SIZE;
}
public long getWritePosition() {
return writePosition;
}
public long getLastFlushFilePosition() {
return lastFlushFilePosition;
}
public long getMAX_FLUSH_DATA_SIZE() {
return MAX_FLUSH_DATA_SIZE;
}
public long getMAX_FLUSH_TIME_GAP() {
return MAX_FLUSH_TIME_GAP;
}
}以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持創新互聯。
文章標題:JavaNIO寫大文件對比(win7和mac)
網站鏈接:http://www.yijiale78.com/article24/jcshce.html
成都網站建設公司_創新互聯,為您提供Google、網站策劃、網站內鏈、App開發、手機網站建設、品牌網站建設
聲明:本網站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如需處理請聯系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創新互聯

- 免費的軟件開發和開源軟件能不能用 2016-08-16
- 成都e代駕APP軟件開發 2022-06-14
- 成都軟件開發企業定制軟件只是一個開始 2022-05-28
- 成都app軟件開發公司需要做的準備工作 2022-08-04
- APP軟件開發為什么那么貴,具體貴在哪里? 2020-11-13
- 行業軟件開發遇到問題該如何解決 2022-07-18
- 如何讓App軟件開發流程更科學 2022-05-07
- 電商APP軟件開發優勢? 2023-03-25
- 如何登陸網站ftp賬號?ftp賬號是什么意思 2021-05-06
- 手機app軟件開發應該有一個硬性的考核指標 2016-08-23
- 軟件開發和網站開發哪種好?兩者有什么區別? 2022-05-29
- 目前制作APP軟件開發的市場還是很龐大的 2021-06-03